ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION OF THE MEDIAN NERVE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
Median nerve (MN) compression neuropathy (CN) at the carpal tunnel (CT) level goes up to 90 % of all tunnel neuropathies. Instrumental methods of examination that are used to diagnose this pathology are electromyography (EMG) and ultrasound (US).
Published: 09.11.2022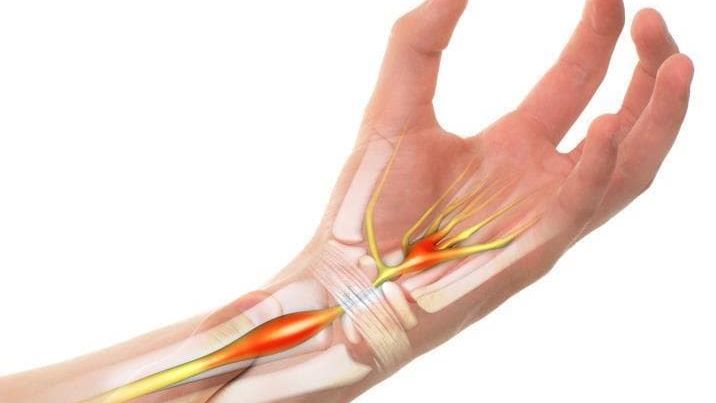
УДК 616.8-073.432.19:617.576](045)
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15674/0030-59872020336-43
ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION OF THE MEDIAN NERVE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
L. I. Klymchuk, O. H. Haiko, R. V. Luchko, Y. I. Halii, S. V. Tymochenko
SI «Institute of traumatology and orthopedics of National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine», Kyiv
Median nerve (MN) compression neuropathy (CN) at the carpal tunnel (CT) level goes up to 90 % of all tunnel neuropathies.
Instrumental methods of examination that are used to diagnose this pathology are electromyography (EMG) and ultrasound (US). Objective: to systematize diagnostic possibilities and to determine the value of US for the patients with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Methods: 99 patients (160 MN) of the main group with CTS (38 — unilateral, 61 — bilateral) clinical signs were analyzed. Control group included 35 patients (70 MN) without symptoms of CTS. Patients were examined clinically and with US on «Esaote MyLab 20 Plus» and PHILIPS HD 11 XE with a 5–12 MHz multi-frequency sensor. Cross-sectional nerve area (CSNA), flattening coefficient (FC), nerve deformation index (NDI), thickness of transverse carpal ligament, its shape, contours, nerve structure, median nerve and carpal ligament echogenicity were studied. EMG was performed in 64 (64.7 %) patients. Thresholds of sonographic parameters for the diagnosis of CTS were determined with ROC analysis with sensitivity and specificity calculation. Results: main qualitative ultrasound parameters of CTS were: change of nerve shape and decreased echogenicity with loss of structural pattern. CSNA in main group was (14.1 ± 4.59) mm², and control — (8.32 ± 1.92) mm², FC — 3.02 ± 0.63 and 2.48 ± 0.60, NDI — 1.21 ± 0.09 and 1.03 ± 0.06, respectively. Optimal threshold level for CSNA was value ˃ 10 mm², FC — ˃ 2.73; NDI — ≤ 1.09 (sensitivity 84.3; 68.0; 81.7 %, respectively). Total frequency of concomitant pathology in main group was 54 (33.8 %) cases, in control group — 13 (18.6 %) (p < 0.02). Conclusions: ultrasound is objective and valuable method to diagnose MN compression neuropathy at the CT level and allow to assess the adjacent structures.
- Tag:
- carpal tunnel syndrome
- tunnel neuropathy
- median nerve
- ultrasound diagnostics
- orthopedics
- neurology
- L. I. Klymchuk
- O. H. Haiko
- R. V. Luchko
- Y. I. Halii
- S. V. Tymochenko